Premium Metal 3D printing
Services In Australia
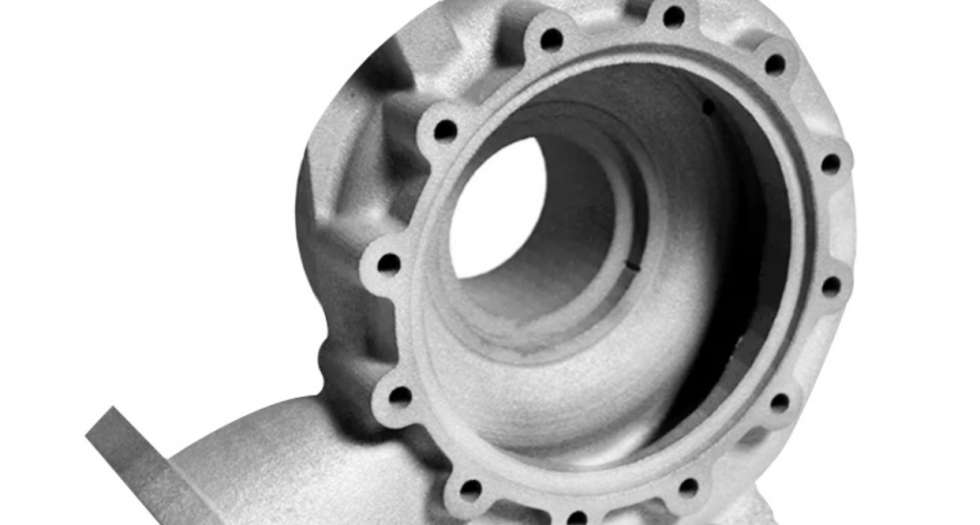
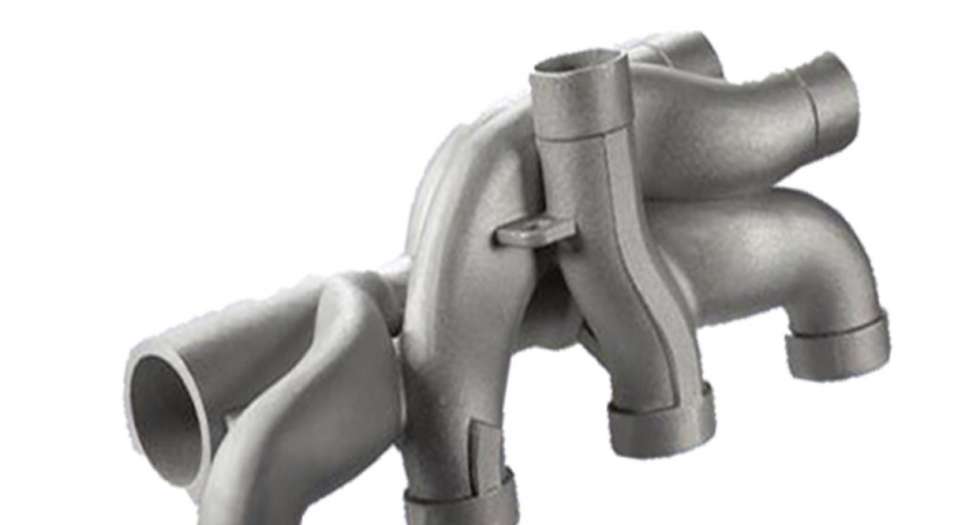
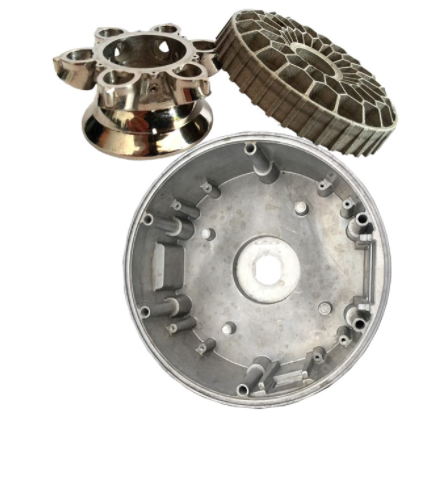
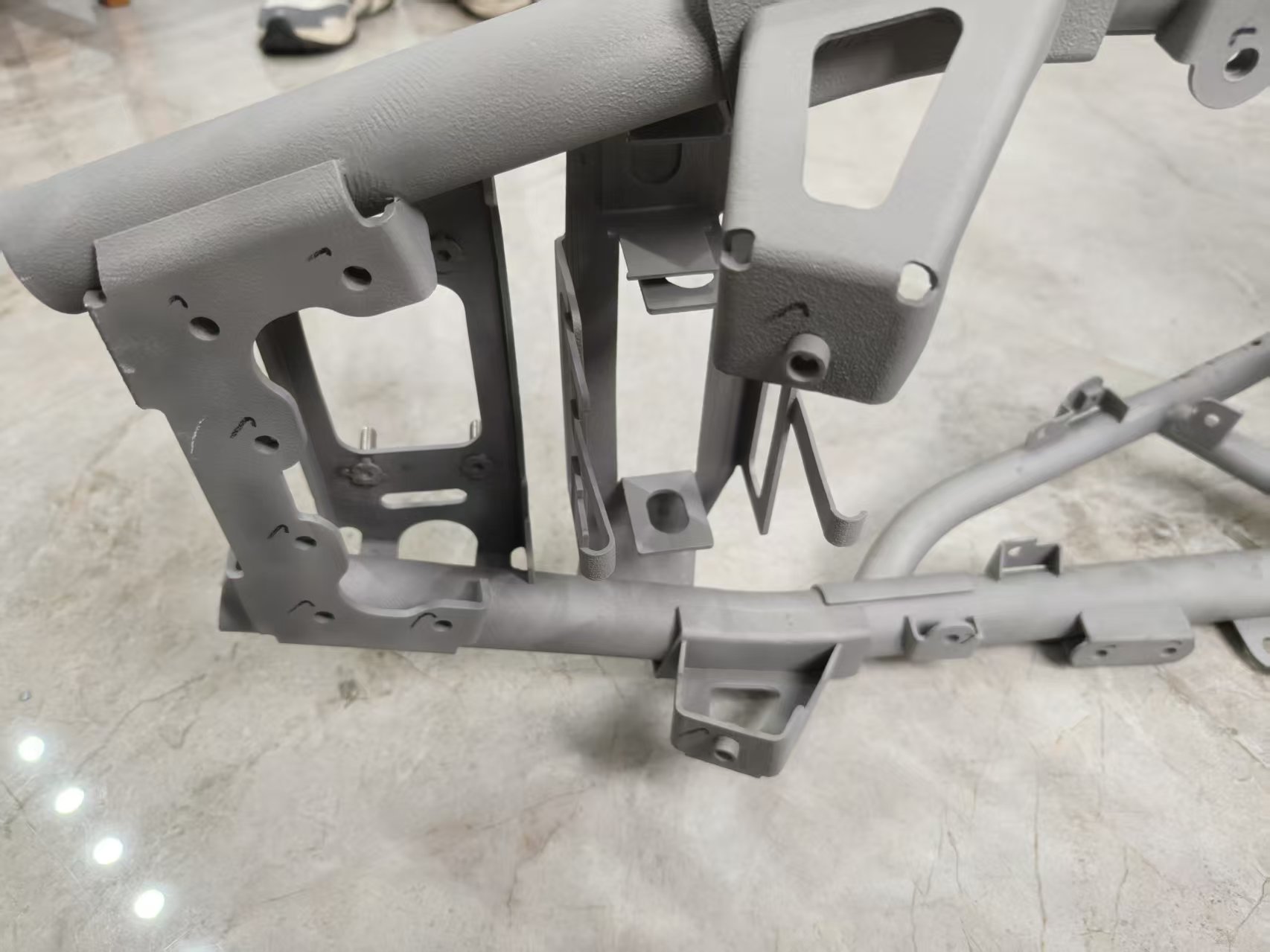
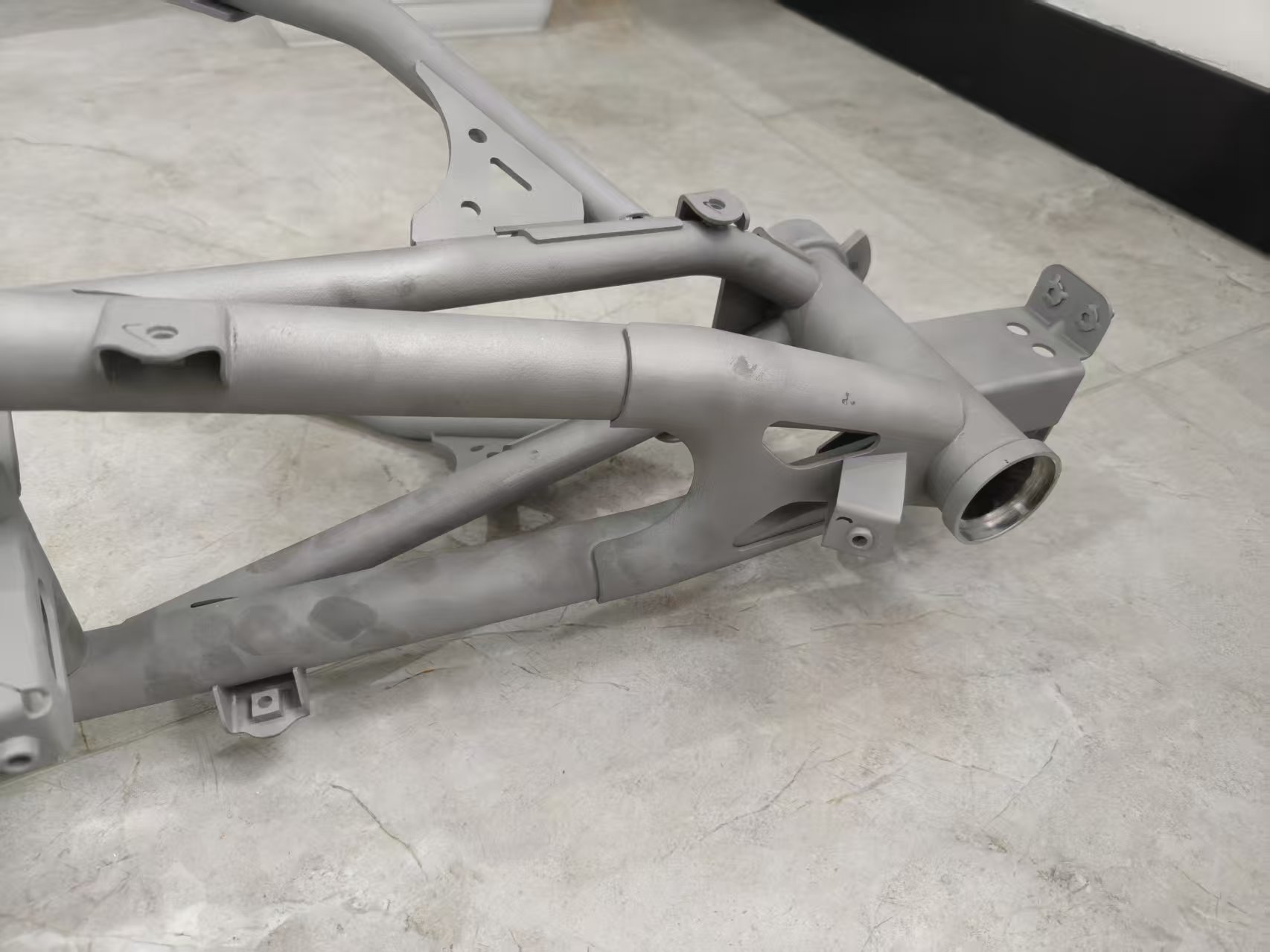
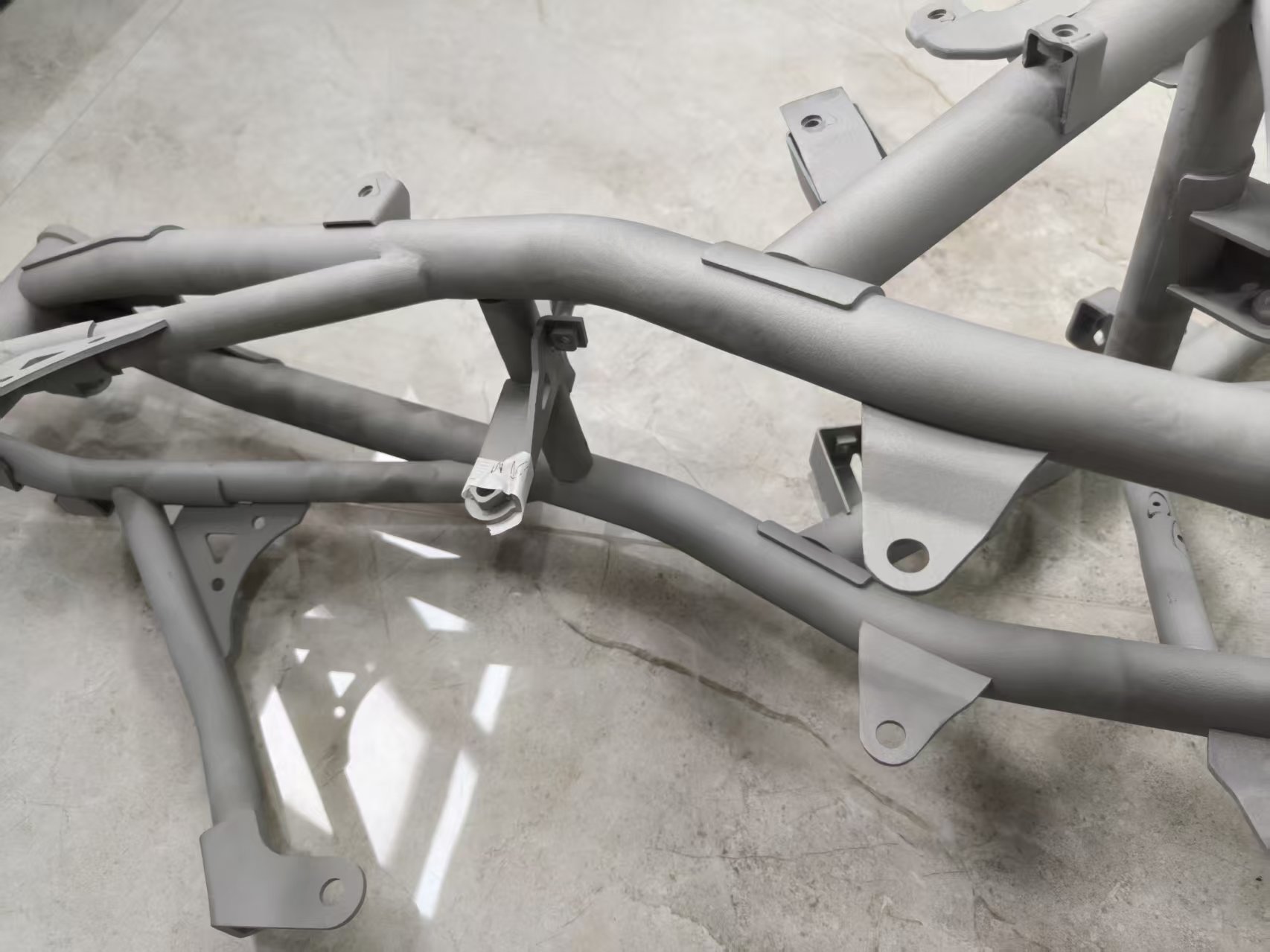
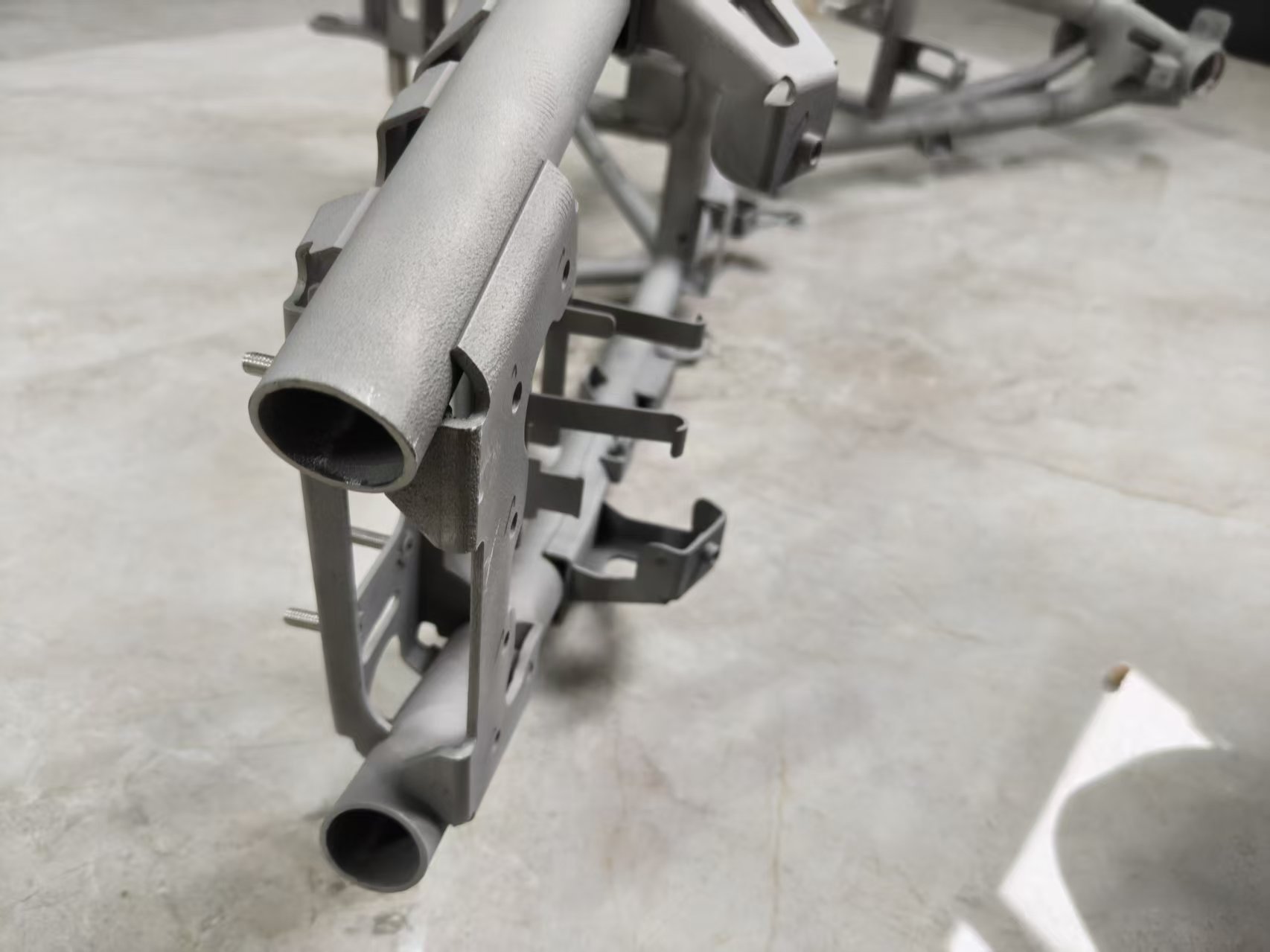
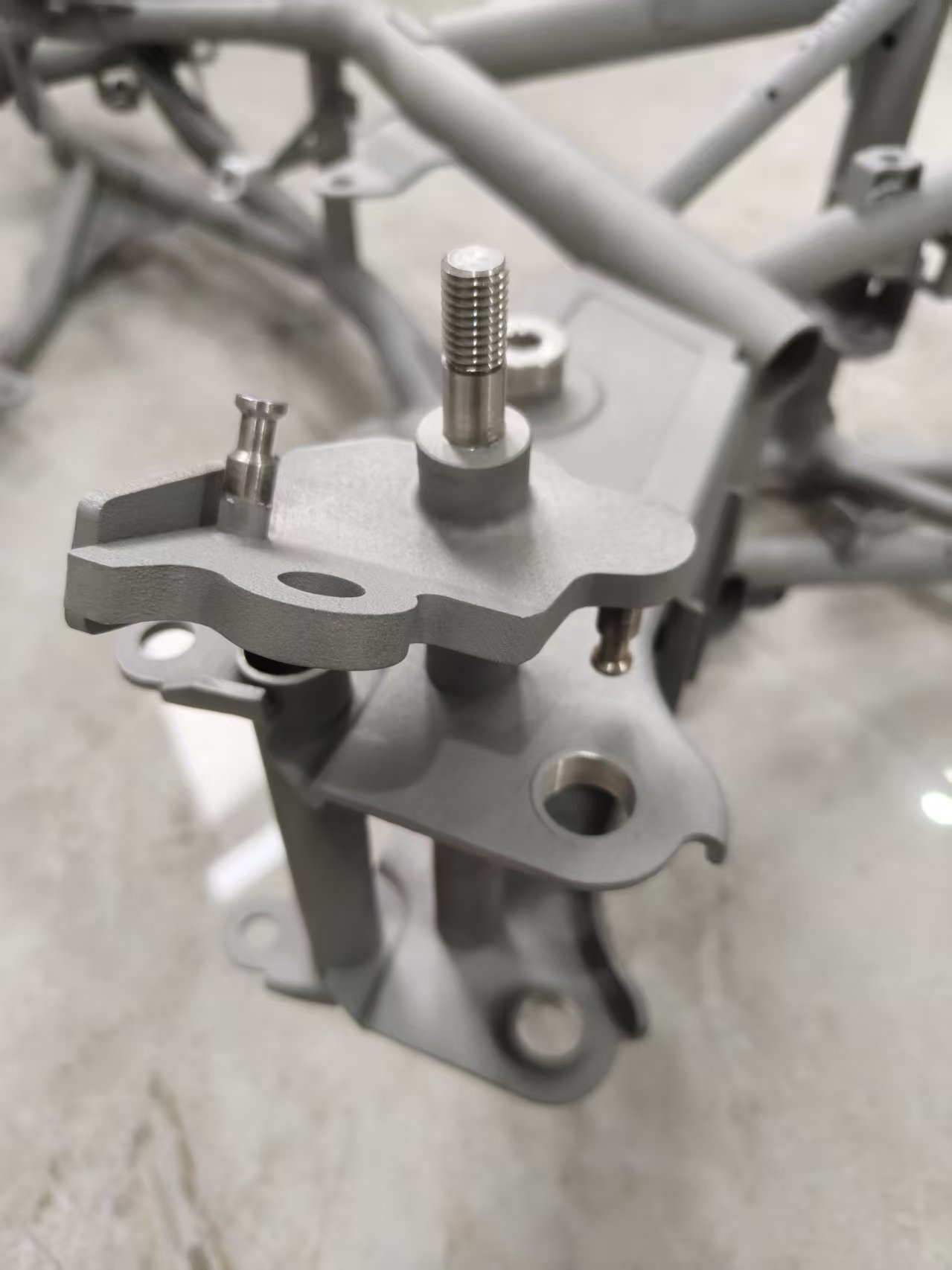
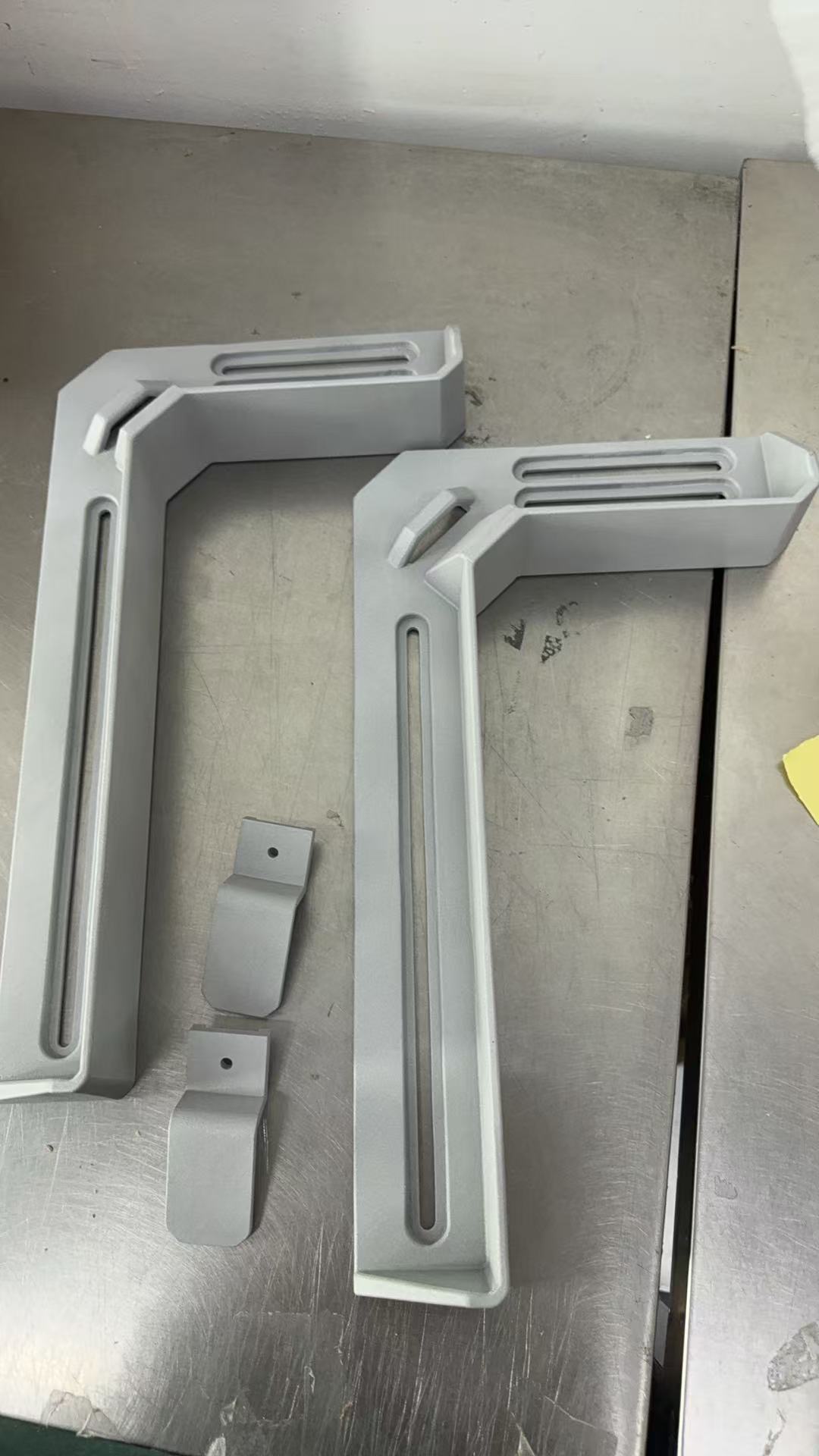
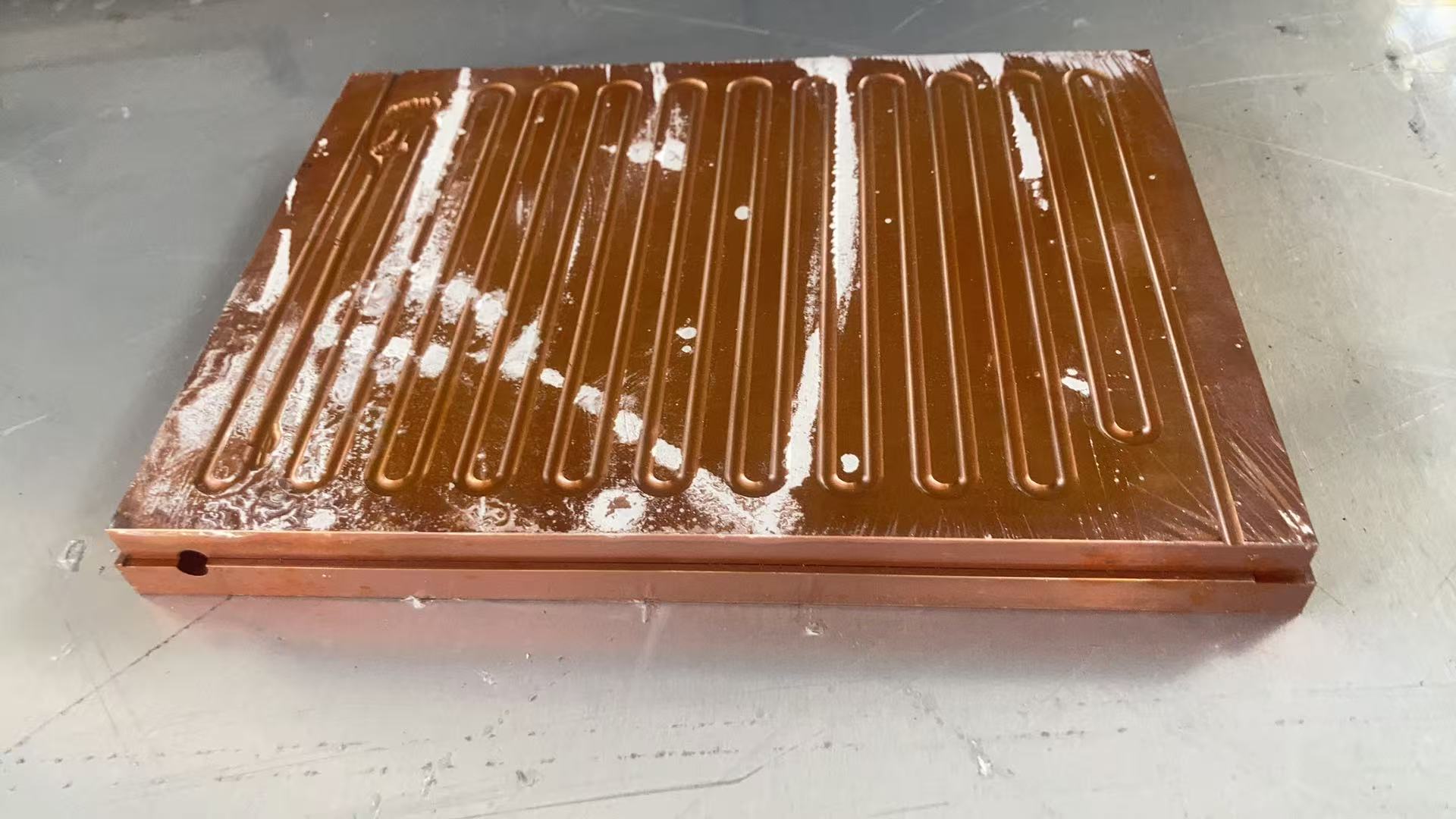
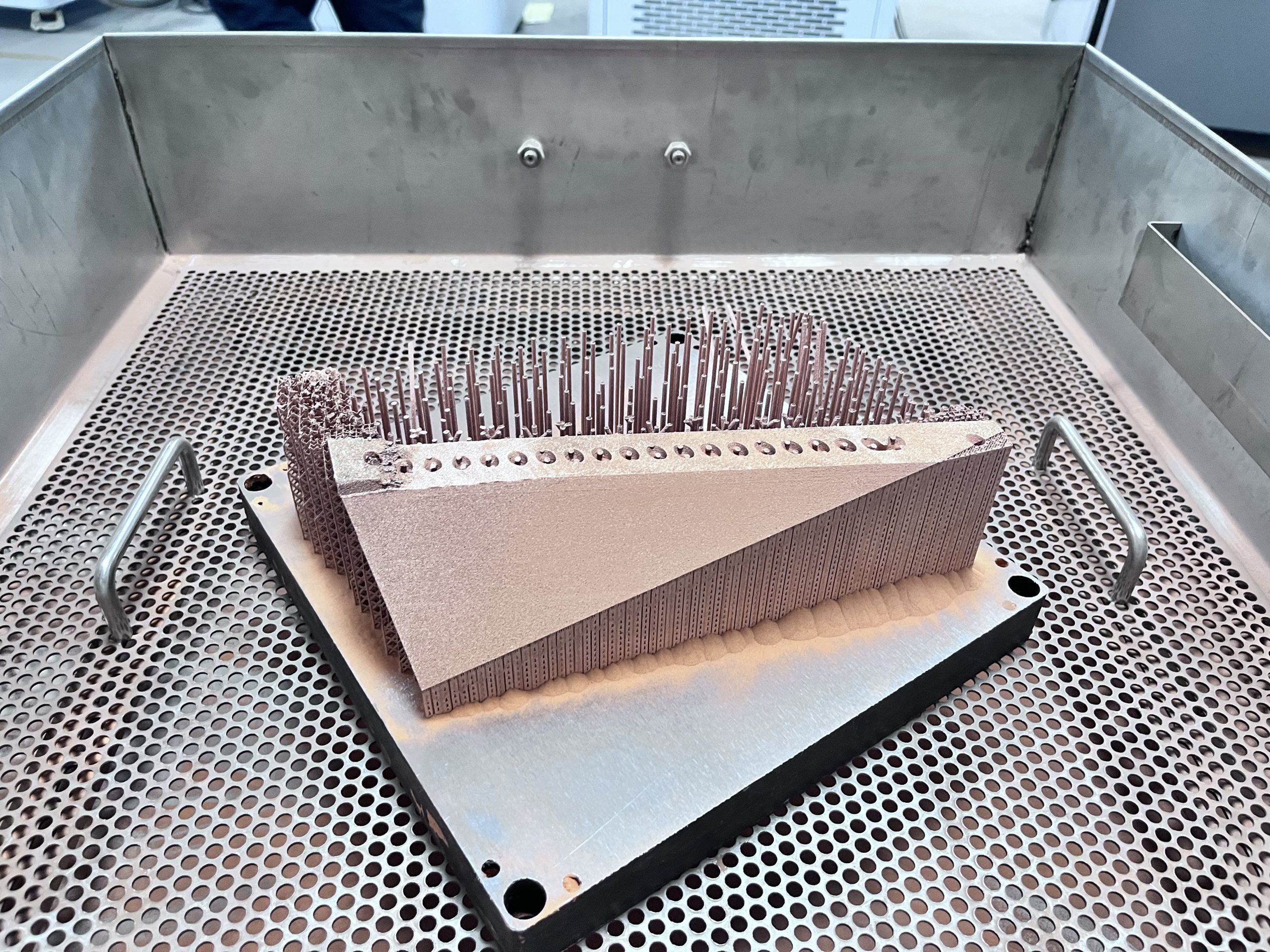
Our 3D Metal Printing Services are an intricate process that uses a layer-based technique to create metal objects in three dimensions. The process resembles another intricate process called Laser sintering; however, it isn’t exactly the same. Here we use high powered lasers to create metal 3D models for our clients. The process uses the lasers to work up the metal and club the substances to bring digitally designed objects to physically printed metal 3D objects.
Trusted Partnerships with Unrivaled Track Record























How Does Our Company Work?
Our company works by providing our customers with 3D printing services tailored to their specific needs. We utilize the latest technologies, 3D printers, and inks to produce high-quality products. Our experienced technicians and 3D printers are capable of producing parts with complex shapes and designs quickly and accurately.
Upload CAD file
Securely upload your part design to our online quote builder.
Confirm specs
Configure your part specifications and select a lead time that suits your schedule.
Receive instant quote
Upload your CAD to our online quoting platform
Manufacturing
We select the best manufacturer for your order, and production begins immediately.
Quality control
We take full responsibility for making sure your parts are manufactured according to our standards
Delivery
Understanding the 3d metal printing technologies: SLM and DMLS
3D Metal printing is done using two primary technologies; SLM and DMLS. Let’s take a dig deep and understand the mechanisms behind the mentioned technologies.
DMLS stands for Direct Metal Laser Sintering. We efficiently deploy DMLS to produce great 3D print Metal models for our clients. The mechanism of DMLS is simple. It uses powdered metal that’s used with the right valuations of heat and pressure to produce 3D printed metal parts. The levy this process offers is that it can be conducted with any alloy. This offers the immense possibility to produce metal 3D goods, unlike other procedures which only work with certain types of metal powders or alloys. The procedure happens by layering the parts that are fused together and left to cool down. Once it cools off, the part becomes ready to use.

Selective Laser Melting, commonly known as SLM, is another one of our expertise that’s held under our belts. We have produced 3D printed metal designs for many of our clients with absolute precision via Selective Laser Melting.
SLM works on with the most common powder materials, including nickel-based alloys, aluminium alloys, steel and iron-based alloys, and more. The results produced through SLM on the powder materials are absolutely phenomena.
SLM uses very high energy, and that’s the reason why it offers absolute precision due to high energy, the metal powder is completely made into a liquid form. That’s what makes it easy to work with. The metal liquid is then layered up to produce the product our clients like or what they order.
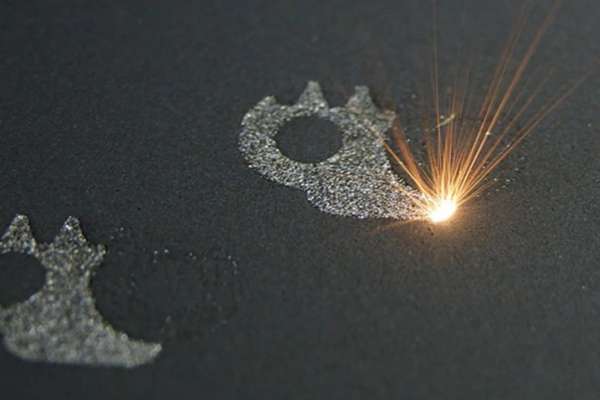

Benefits of Direct Metal Laser Sintering
There are several benefits that you can avail by having 3D printing Metal via DMLS by us. Down below, we shall discuss a few:
Direct metal Printing– one reason why this method is so efficient is that it offers 3D metal printing without affecting the properties. So you get actual and workable properties of alloys and raw metal parts that you order us to make.
Recyclable material- Wastage is a very common industrial problem. Millions of dollars are lost due to the wastage of powdered metal. However, with DMLS, we can easily reuse the powdered metal that didn’t melt or get sintered. This also results in negligible wastage of resources.
Vital Functional Parts- With DMLS, workflow is super-efficient because several parts can be worked upon at the same time!
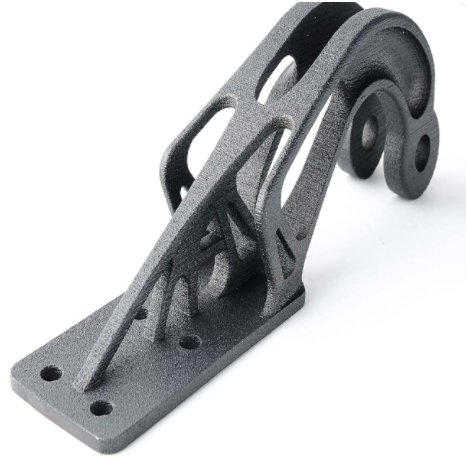

Down below are some key features of the DMLS 3D printing:
- You get good quality and fully functional 3D printed metal parts made with DMLS
- Adjustable volumes are one of the greatest offerings of the procedure. The method offers the making of several different parts at one single time rather than having to wait to finish one thing before getting on with the other.
- Best finishes are one thing that we take pride in. With DMLS, we are able to deliver stellar and shiny metal products by using several processes after the metal part is 3D printed, such as anodizing, electroplating or powder coating.

So if you are looking to get Metal 3D printing in Perth, Brisbane, Adelaide & Australia overall, then we are up to be of assistance. We champion this art and have delivered pristine products and designs to our clients. Our motto is simple, to deliver the best products. That’s the reason why we have well-trained employees who work on the best machines available to us.
Allow us to metal print your designs. We assure you that you’ll be delighted by the results we produce for you!
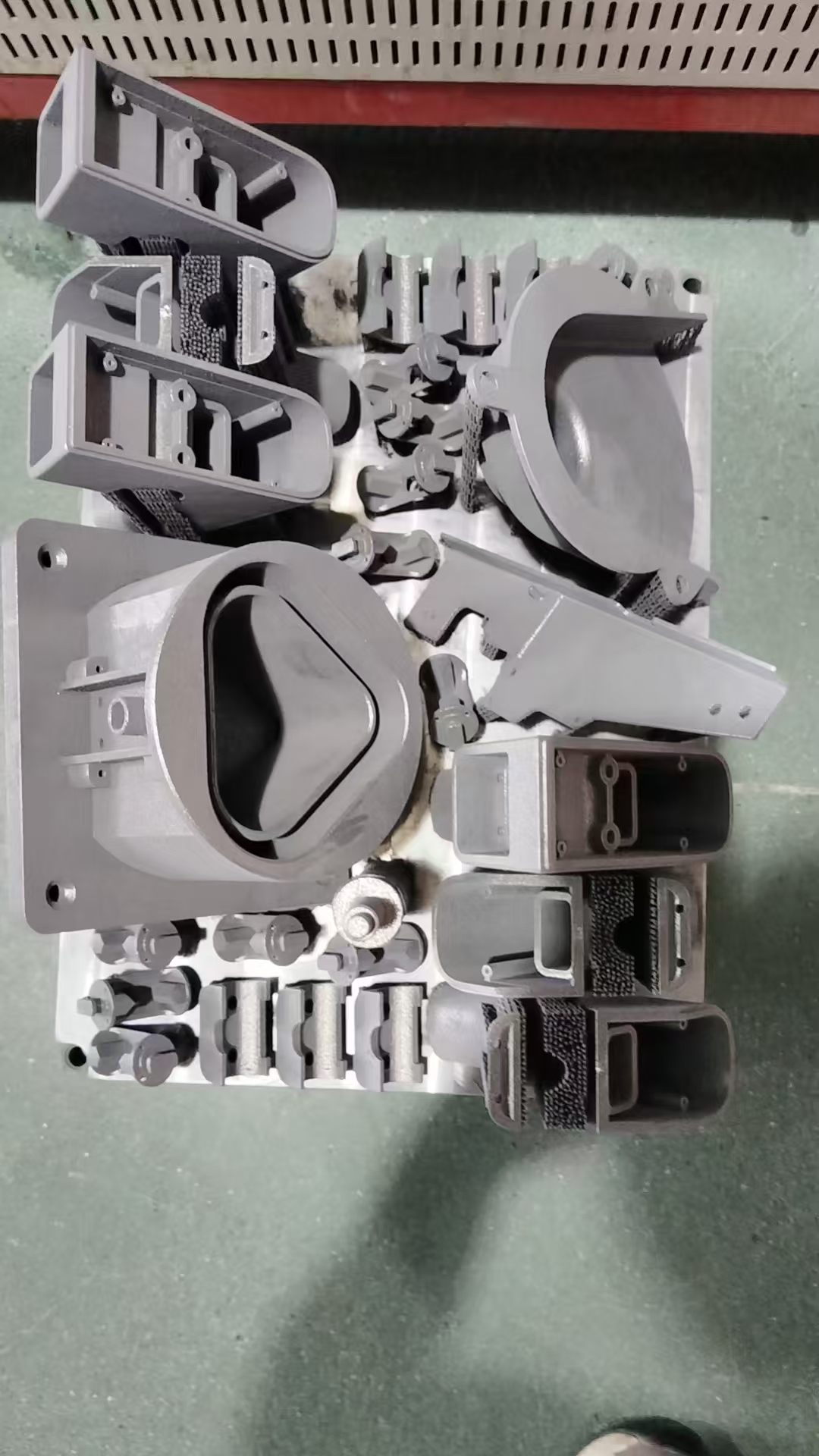
We have a wide range of 3D Printing Materials Metal. You can get any sort of design produced by us. Be it prototyping or mass production; we are well equipped to cater to any challenge that you throw our way!

Cities We Cover
We have become a renowned brand in Australia to get your metal 3D printing projects done. We have been serving the top cities in Australia, i.e. Sydney, Perth, Melbourne and Brisbane.
No matter how complex your metal printing project seems, our metal 3D printing experts in Sydney will provide you with your desired product as quickly as possible.
No matter what your requirements are, we have qualified people in Canberra and always committed to give you an expert advice and superior quality workmanship.
The precision that our metal 3D printing team has shown over time has made us the top choice for industries to metal print their designs.
Our metal 3D printing experts in Brisbane have been in the limelight of industry owners to get their metal printing tasks done quickly and efficiently.
Our metal 3D printing experts in Adelaide ensure the provision of the maximum durability and premium quality finish, regardless of your object and project.
Industries we serve with metal printing

Materials used in the Metal Printing Process
This material has good thermal and mechanical properties and low density. This metal also has high electrical conductivity.
This metal has high resistance and hardness. It is widely used in food and medica sector.
It is widely used in wiring and cabling and electronic industry.
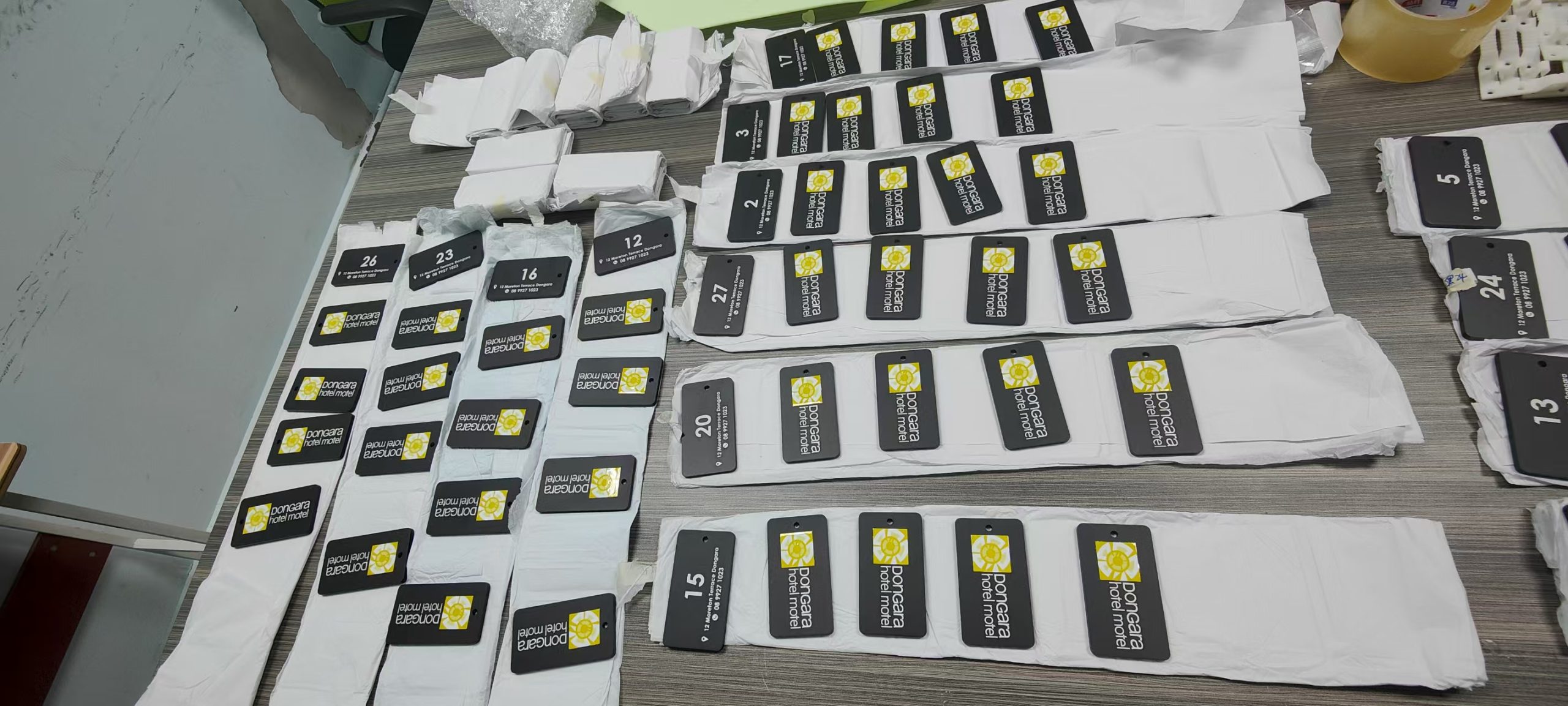
Brass printing is widely used in 3d printing jewelry, accessories and other decoration items.
It is widely used in 3d printing jewelry and decorative objects.
This technology regenerates real 3D parts from layer-by-layer additions of fused metal powder.
Metal Printing Methods
| Material Name | Quality | Min Details | Minimum Wall Thickness | Maximum Size |
Metal Laser Sintering (Metal) Stainless steel 316L | Smooth finish | 0.1mm | 1mm | 220x220x250 |
Stainless Steel420 (SLM) | Smooth finish | 0.2mm | 1.5mm | 760×390×390mm |
Aluminium | Smooth finish | 0.2mm | 1.5mm | 270x220x320mm |
Stainless Steel316L (DMLS) | Smooth finish | 0.1mm | 1mm | 220x220x250mm |
MS1 Steel (DMLS) | Smooth finish | 0.1mm | 1mm | 220x220x250mm |
Brass | Ultra Smooth Surface | 0.1mm | 0.8mm | 89x89x100mm |
Bronze | Ultra Smooth Surface | 0.1mm | 0.8mm | 89x89x100mm |
Copper | Ultra Smooth Surface | 0.1mm | 0.8mm | 89x89x100mm |